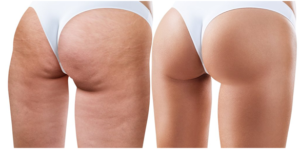
Cellulite is the herniation of subcutaneous fat within fibrous connective tissue that manifests as skin dimpling and nodularity, often on the pelvic region (specifically the buttocks), lower limbs, and abdomen. Cellulite occurs in most postpubescent females.

A variety of treatment approaches are available to improve the appearance of cellulite, at least temporarily. Each has its own set of potential results and side effects. Some studies indicate that a combination of treatments may yield the most satisfying results.
- Laser and radiofrequency treatments. Various wounding (ablative) laser treatments are available to treat cellulite. In one method, a thin fiber is slipped under the skin to deliver laser heat that destroys the fibrous bands binding fat. This approach has shown to reduce the appearance of cellulite for six months to a year. Further study is needed.
There’s also a device that uses heat (radiofrequency) for nonablative treatment that improves how the skin looks. You’ll likely need several sessions before you notice an improvement in the appearance of your skin. Nonablative treatments typically need to be repeated more often than do ablative treatments.
- Cryolipolysis. With cryolipolysis (CoolSculpting), fat below the skin is reduced with a device that uses vacuum suction to raise tissue into contact with cooling plates. You’ll need multiple treatments. Results appear gradually over two to three months.
- Acoustic wave therapy. With this technique, a technician applies gel to the affected skin and runs a small, hand-held device (transducer) over the area. The transducer sends sound waves into your body, breaking up cellulite. You’ll likely need several sessions before you notice an improvement in the appearance of your skin.
- Surgery. Your doctor may offer one of various procedures that use needles, blades or other special tools to separate the fibrous bands under the skin (subcision) in an effort to smooth the skin. One method also uses fat grafting to improve skin appearance. Results from these techniques may last two to three years.
Complications of these techniques may include pain and bleeding beneath the skin.