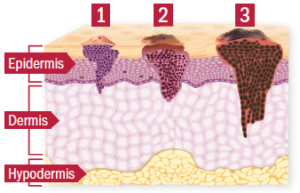
Skin cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin.
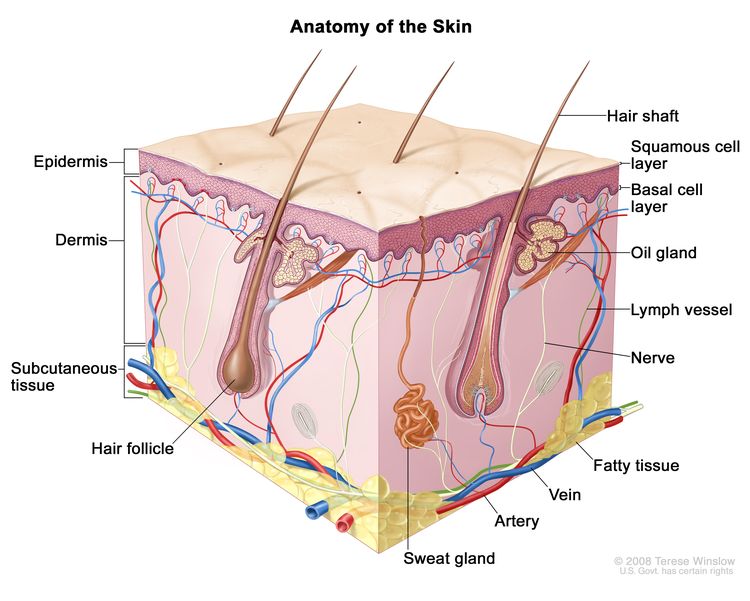
The skin is the body’s largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D. The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis (upper or outer layer) and the dermis (lower or inner layer). Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
There are different types of treatment for patients with basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis.
Eight types of standard treatment are used:
-
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Photodynamic therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Chemical peel
- Other drug therapy
There are different types of treatment for SKIN TUMOR
Different types of treatment are available for patients with basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, and actinic keratosis. Some treatments are standard (the currently used treatment), and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.